FAQs
Most frequent questions and answers
FAQs Engineered Timber Flooring
Engineered timber flooring is a type of flooring material that consists of a real timber veneer/lamella layer bonded to multiple layers of plywood, blockboard or high-density fiberboard (HDF), as opposed to solid timber flooring, which is one single layer of solid timber. It is designed to provide the aesthetic appeal of solid timber flooring while offering greater structural stability and resistance to moisture-related issues.
The construction of engineered timber flooring typically involves a top layer of a timber veneer/lamella, which can be made from various timber species such Spotted Gum, Blackbutt and European Oak. This veneer/lamella gives the floor its authentic timber appearance. Below the veneer/lamella, there are several layers of plywood, blockboard or high-density fiberboard (HDF) that are arranged in a cross-grain pattern. This cross-grain construction helps to minimize the expansion and contraction of the flooring due to changes in temperature and humidity, making it more dimensionally stable and less susceptible to cupping, crowning, warping and bowing than then solid timber.
One of the key advantages of engineered timber flooring is its versatility. It can be installed in various settings, including areas where solid timber may be more prone to issues, such as rooms with fluctuating humidity levels. Additionally, engineered timber flooring is often available in a variety of styles, finishes, and sizes, providing homeowners with a wide range of options to suit their preferences and interior design needs.
Overall, engineered timber flooring combines the natural beauty of timber with enhanced durability and stability, making it a popular choice for many residential and commercial applications and is highly suitable to the temperamental Australia climate.
In summary, while the core layers may be composed of other materials, the top layer of engineered timber flooring is genuine timber, making it a real timber product with the aesthetic appeal of natural timber with greater dimensional stability than solid timber.
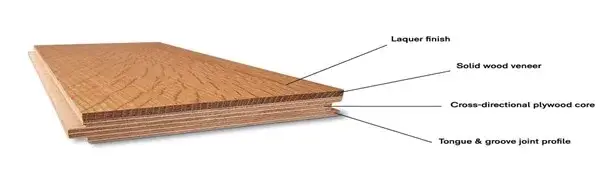
Engineered timber flooring offers several benefits, making it a popular choice for many homeowners. Some of the key advantages include:
- Durability: Engineered timber flooring is more resistant to moisture and temperature fluctuations than solid timber. Its layered construction helps minimize the risk of cupping, crowning, warping and bowing, making it a durable option for various environments.
- Stability: The cross-grain construction of engineered timber flooring provides enhanced dimensional stability. This means it is less prone to expansion and contraction, making it suitable for rooms with fluctuating humidity levels and is highly suitable to the temperamental Australia climate.
- Versatility: Engineered timber flooring is far more versatile than solid timber flooring. It can be utilised in a variety of settings where solid timber would not be suitable, as well as a number of applications where solid timber would be less suitable for example on ceilings, walls, cabinetry and joinery applications.
- Aesthetic Appeal: The top layer of engineered timber flooring is real timber, offering an authentic and natural look. It is available in a wide range of timber species, finishes, and styles, allowing homeowners to choose a flooring option that complements their interior design.
- Installation Options: Engineered timber flooring often comes with click-lock or tongue-and-groove systems, making it easier to install than traditional solid timber flooring. Some engineered timber floors are designed to be floated or glued down, providing flexibility in installation methods, being quicker and easier to install than solid timber flooring. Furthermore, selecting a factory finished engineered timber flooring option, removes the need to sand and coat on site, thereby reducing costs and the likelihood of coating issues arising. Being easier to install than solid timber flooring, engineered timber flooring is a perfect product for the DIY market.
- Environmentally Friendly: Engineered timber flooring typically uses less timber than solid timber flooring, making it a more resource-efficient option, reducing deforestation impact. Additionally, the plywood, blockboard or high-density fiberboard (HDF) layers are often made from fast-growing and renewable timber species, making it a more resource-efficient option compared to solid timber flooring.
- Cost-Effective: Engineered timber flooring tends to be more affordable than solid timber flooring options. Engineered timber flooring is cost-effective due to its layered construction, utilizing a thin top layer of real timber over plywood, blockboard or high-density fiberboard (HDF). This design reduces the amount of timber required. Enhanced durability and resistance to moisture also contribute to long-term savings by minimizing the need for repairs or replacements, making it a more financially viable option for homeowners. Finally, the reduced time and effort it takes to install engineered timber flooring as opposed to solid timber flooring, helps to keep the overall costs for a project lower.
- Underfloor Heating: The majority of engineered timber floors are suitable for use with underfloor heating systems, providing a warm and comfortable flooring solution. It is important to check with the manufacture of the engineered timber flooring and adhesives, if their products are suitable for underfloor heating systems.
Overall, the benefits of engineered timber flooring make it a practical and attractive choice for those seeking the look of real timber with added durability, versatility and at a more competitive price point than solid timber flooring.
Here are the benefits of a thicker top wear layer and how its thickness impacts the overall performance of the flooring:
- Extended Lifespan: The additional thickness in the wear layer contributes to a longer lifespan for the engineered timber flooring. This is particularly important in high-traffic areas where the floor is subjected to more stress and potential damage.
- Refinishing Potential: A thicker wear layer allows for multiple refinishing cycles. If the surface shows signs of wear, scratches, or fading over time, the floor can be sanded and refinished to restore its appearance, extending its longevity.
- Stability: The top wear layer influences the stability of the flooring. A thicker top wear layer can provide better resistance to changes in humidity and temperature, reducing the risk of cupping, crowning, warping and bowing, or other forms of distortion.
- Quality Aesthetic Appearance: The thickness of the top wear layer can contribute to the quality and authenticity of the timber’s appearance. A thicker top wear layer often showcases the natural characteristics of the timber more effectively. Often engineered timber flooring with a thicker top wear layer, utilises a saw cut as opposed to a sliced cut, which is a more expensive cut, but provides a far more beautiful aesthetic result.
When considering engineered timber flooring, it’s advisable to assess the thickness of the top wear layer along with the overall construction of the flooring. While a thicker wear layer generally indicates higher quality and durability, other factors such as the core material and manufacturing processes also influence the performance of the flooring. It is also to be noted that the thicker the top wear layer, the deeper any potential indentations, as opposed to a thinner top wear layer.
Engineered timber flooring it is not completely immune to these issues. The extent to which engineered timber flooring may dent or scratch depends on various factors, including the thickness of the top wear layer, the type of timber used, and the overall quality of the flooring. Timber hardness is rated by a Janka Rating, which measures the timber’s resistance to scratching, wearing and denting. The higher the numerical value of the Janka Rating the harder the timber.
Benefits that can contribute to reduced denting and scratching in engineered timber flooring include:
- Timber Species: The type of timber used for the top wear layer influences its hardness. Timber species with greater hardness, such as Spotted Gum and Blackbutt, tend to be more resistant to scratches, wear and dents.
- Protective Finishes: The application of protective finishes, such as lacquer or aluminum oxide coatings, enhances the flooring’s resistance to wear and tear.
- Maintenance and Care: Regular maintenance and proper care, such as using furniture pads, rugs, and avoiding dragging heavy objects across the floor, can help prevent dents and scratches.
It is essential to follow manufacturer recommendations for maintenance and care to ensure the longevity of the flooring. Additionally, no flooring material is entirely impervious to damage, so taking precautions to protect the surface will help maintain its appearance over time.
Engineered timber floors can be considered more environmentally friendly than some alternative, but their sustainability depends on several factors:
- Resource Efficiency: Engineered timber often uses a thinner layer of timber for the top veneer/lamella compared to solid timber floors. This means less of the high-quality wood is required, potentially reducing the overall impact on forests.
- Renewable Materials: The core layers of engineered flooring are typically made from plywood, blockboard or high-density fiberboard (HDF), often sourced from fast-growing and renewable timber species. This can contribute to the sustainability of the product.
- Less Waste: The manufacturing process of engineered timber flooring can result in less waste compared to traditional solid timber, as smaller or lower-grade pieces of wood can be used for the core layers.
- Stability in Various Environments: Engineered flooring’s stability in different humidity and temperature conditions can reduce the likelihood of warping or cupping, potentially leading to a longer lifespan and less need for replacement.
FAQs SPC Hybrid Vinyl Flooring
- SPC (Stone Plastic Composite): SPC hybrid vinyl flooring is a type of rigid core vinyl flooring that is made from a blend of natural limestone powder, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and stabilizers. The result is a durable and rigid plank that is resistant to water and can handle heavy foot traffic. SPC hybrid vinyl flooring is known for its water resistant properties, stability and ability to withstand temperature variations.
- Hybrid Vinyl Flooring: The term “hybrid” typically refers to a combination or blend of different materials or technologies. In the context of vinyl flooring, hybrid vinyl may refer to a flooring product that combines features from various types of vinyl flooring, such as SPC and WPC.
SPC hybrid vinyl flooring is made up of several layers, each with its own important function:
- Wear layer: The top layer is a clear, protective wear layer made of PVC or polyurethane. This layer protects the floor from scratches, stains, and fading.
- Printed vinyl layer: The second layer is a printed vinyl layer that gives the floor its design. This layer can be made to look like timber or any other type of flooring.
- SPC core: The third layer is the SPC core, which is made of stone plastic composite. This layer is what gives the floor its strength and rigidity.
- IXPE backing:The fourth layer is an IXPE backing, which is a type of foam that helps to provide sound insulation and comfort underfoot.
Here are some advantages of SPC hybrid vinyl flooring:
- Water Resistant: SPC hybrid vinyl flooring is highly resistant to water.
- Durability: SPC hybrid vinyl flooring is known for its durability and resistance to dents, scratches, and stains. It can withstand high traffic areas and is a suitable option for commercial as well as residential spaces.
- Stability and Rigidity: The stone composite core gives SPC hybrid vinyl flooring exceptional stability and rigidity, preventing the expansion and contraction that can occur with temperature fluctuations. This makes it a good choice for areas with varying temperature conditions and is highly suitable to the temperamental Australia climate.
- Easy Installation: SPC hybrid vinyl flooring features a click-lock system, making it easy to install without the need for adhesives. It is a DIY-friendly option, saving both time and installation costs.
- Comfort and Sound Insulation: SPC hybrid vinyl flooring provides a comfortable underfoot feel and offers excellent sound insulation, reducing the impact noise caused by footsteps.
- Low Maintenance: SPC hybrid vinyl flooring is easy to clean and maintain. Regular sweeping and occasional lightly mopping are usually sufficient to keep it looking in pristine condition.
- Wide Range of Styles: SPC hybrid vinyl flooring comes in a variety of styles, colours, and patterns, allowing for a customizable and aesthetically pleasing flooring option that can mimic the look of timber or any other type of flooring.
- Health and Safety: SPC hybrid vinyl flooring is often free from harmful chemicals like phthalates and formaldehyde, making it a safer choice for indoor air quality.
- Affordability: SPC hybrid vinyl flooring is generally more affordable compared to some other flooring options like timber or stone.
- Environmentally Friendly: SPC hybrid vinyl flooring is often considered more environmentally friendly than some alternatives, as it is recyclable and doesn’t require the harvesting of natural resources like timber.
SPC hybrid vinyl flooring is known for its durability and resistance to scratches, wear, and dents. It is composed of a rigid core layer that typically includes limestone and stabilizers, providing a strong and stable foundation. The wear layer on top of the core is usually treated with a protective coating, such as a UV-cured urethane coating, which enhances the flooring’s resistance to scratches and wear.
While SPC hybrid vinyl flooring is generally more resistant to scratches, wear, and dents compared to traditional vinyl or timber flooring, it’s important to note that no flooring material is completely immune to damage. The level of durability can also vary based on the quality and thickness of the wear layer.
To maximize the lifespan and performance of SPC hybrid vinyl flooring, it’s recommended to follow proper maintenance practices, such as using furniture pads, avoiding dragging heavy objects, and keeping the floor clean from abrasive particles. It is essential to follow manufacturer recommendations for maintenance and care to ensure the longevity of the flooring.
SPC hybrid vinyl flooring is generally considered more environmentally friendly than some traditional flooring options. Here are some factors to consider:
- Recyclable Materials: SPC hybrid vinyl flooring often incorporates limestone, which is a natural and abundant resource. Some manufacturers may also use recycled materials in the production of SPC flooring, making it a more sustainable option.
- Low VOC Emissions: Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) are chemicals that can be emitted from certain materials and may contribute to indoor air pollution. Many SPC hybrid vinyl flooring products are designed to have low VOC emissions, which is beneficial for indoor air quality.
- Energy Efficiency: Some manufacturers prioritize energy-efficient production processes, which can contribute to the overall environmental friendliness of SPC hybrid vinyl flooring.
- Longevity and Durability: SPC flooring is known for its durability and long lifespan. Products that last longer generally require fewer replacements, reducing the overall environmental impact associated with manufacturing, transportation, and disposal.
